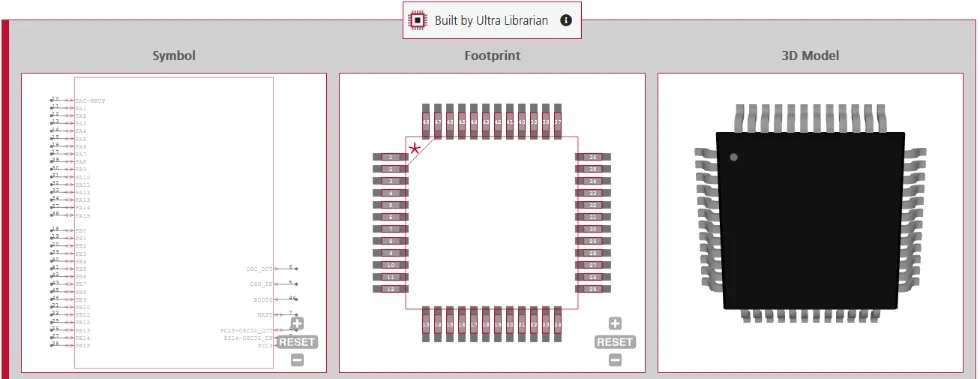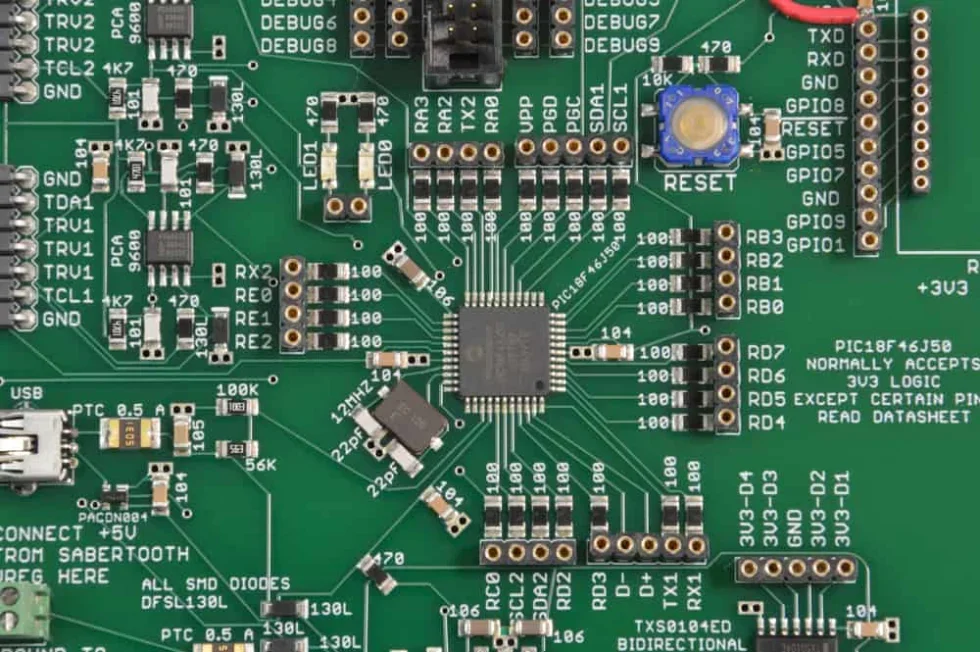
Many PCBs require that you choose the best SMT and THT components for your design
Choosing between surface-mount technology (SMT) and through-hole technology (THT) components is a critical decision that directly impacts PCB design success, manufacturing costs, and product reliability. In many cases, your design will include both types. Therefore, understanding the fundamental differences between SMT and THT components is crucial to selecting the best components, which will also determine the manufacturing requirements to optimize the assembly of your PCB.
Understanding SMT and THT Component Attributes
Many through-hole and surface mount devices (SMDs) have similar performance profiles. In fact, most major manufacturers produce both types, especially when it comes to passive components. Consequently, you must look beyond electrical characteristics to determine which is the best option for your design. The following are some important differentiating factors to consider.
| Attributes of SMT and THT Components | ||
| Factor | SMT Components | THT Components |
| Availability | Extensive selection, dominant in the market | Limited selection for newer technologies |
| Cost | Lower component cost, higher setup cost | Higher component cost, lower setup cost |
| Ease of Manufacturing | Automated pick-and-place assembly | Manual insertion required |
| Component Density | High density, both-sided mounting | Low density and single-sided are typical |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower mechanical bond strength | Superior mechanical connection strength |
| Routing Complexity | Complex routing with via-in-pad capability | Simplified routing requires drilled holes |
| Rigid PCB Compatibility | Excellent compatibility | Excellent compatibility |
| Rigid-Flex PCB Compatibility | Excellent on rigid sections only | Limited, typically rigid sections only |
| Flex PCB Compatibility | Limited, requires careful consideration | Not recommended for flexible areas |
As illustrated in the table, several factors can help you choose the right component type for your design. However, to make a fully informed decision, it is important to understand the advantages and disadvantages of both SMT and THT components.
SMT Components: Advantages and Disadvantages
| SMT Advantages | SMT Disadvantages |
👍Higher Component Density: SMT components enable up to 60-70% PCB size reduction compared to through-hole designs. Components can be mounted on both sides of the board, maximizing space utilization for compact product designs.
👍Enhanced High-Frequency Performance: Shorter lead lengths reduce parasitic inductance and capacitance, making SMT components ideal for high-frequency applications where signal integrity is critical.
👍Manufacturing Efficiency: Automated pick-and-place assembly significantly increases production speed while reducing labor costs. The highly automated SMT process enables consistent, repeatable manufacturing at scale.
👍Cost-Effective Production: While the initial equipment investment is substantial, SMT assembly offers lower per-unit costs through automation, material savings, and increased throughput for high-volume production. | 👎Complex Repair Requirements: SMT component repair demands specialized equipment, including hot air rework stations and microscopes, which increases maintenance complexity and costs.
👎High Initial Investment: Setting up SMT assembly lines requires significant capital investment in pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and inspection equipment, creating barriers for smaller manufacturers.
👎Environmental Sensitivity: SMT components exhibit increased susceptibility to mechanical stress and thermal cycling compared to through-hole alternatives, which can potentially impact their reliability in harsh operating conditions.
👎Manual Assembly Challenges: The small size of SMT components makes manual prototyping and small-batch assembly difficult without specialized tools and techniques. |
THT Components: Advantages and Disadvantages
| THT Advantages | THT Disadvantages |
| 👍Superior Mechanical Strength: THT components create robust mechanical bonds by passing their pins through the PCB and soldering on both sides. This construction provides exceptional resistance to mechanical stress, vibration, and physical shock.
👍Simplified Prototyping: 👍High-Power Capability: 👍Environmental Reliability: | 👎Increased PCB Size: The drilled holes and larger component footprints result in significantly larger board sizes, limiting miniaturization potential for compact device designs.
👎Higher Production Costs: 👎Limited Component Density: 👎Slower Manufacturing: |
Guidelines for Choosing Between SMT and THT Component Types
As discussed above, there are many factors and comparison criteria to consider when choosing between SMT and THT components. To best put this understanding into practice, we have provided guidelines that you can use to base your selection process.
SMT and THT Components: Selection Guidelines
|
The choice between SMT and THT components fundamentally depends on balancing project requirements, including size constraints, power requirements, environmental conditions, production volume, and manufacturing capabilities. SMT dominates modern electronics through its superior density and automation benefits, while THT remains essential for applications that demand mechanical robustness and high-power handling. Successful PCB design depends on how well you leverage both technologies strategically to optimize performance, cost, and manufacturability for their specific application requirements.
If you’re looking for CAD models for common components or important information on how to choose between SMT and THT components, Ultra Librarian helps by compiling all your sourcing and CAD information in one place.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.