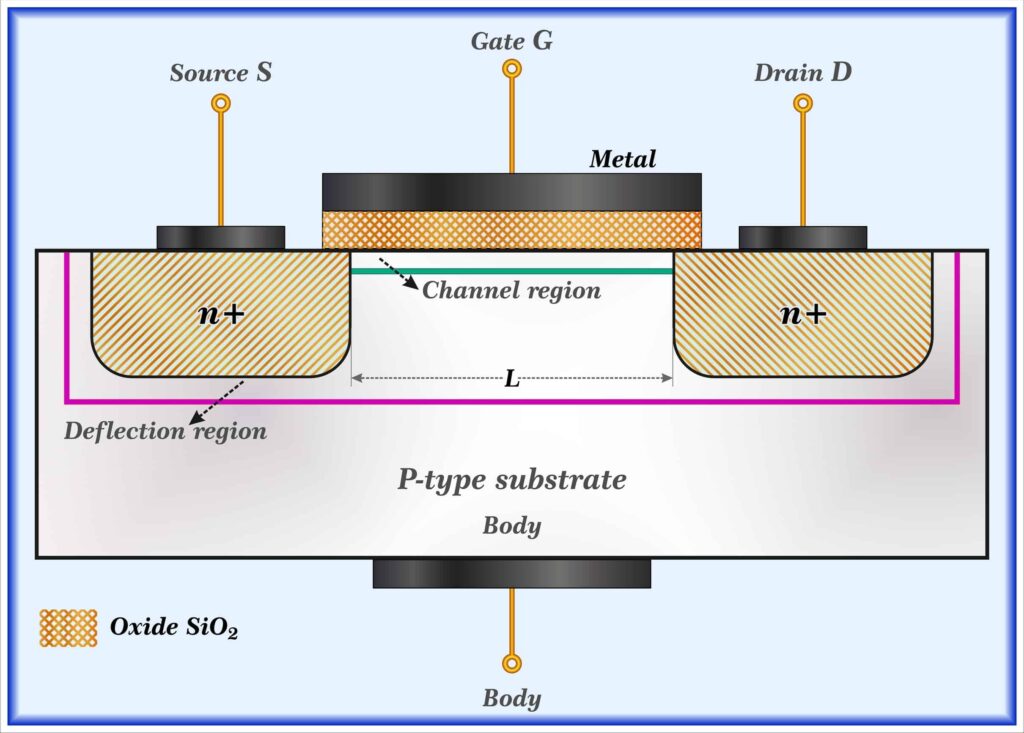
N-Channel MOSFET enhancement mode
Transistors are one of the essential devices for electronics. These semiconductors are prolific in both analog and digital circuit designs. Although bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) (the first transistor architectures) and junction field-effect transistors (JFETs) are commonly used, metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are the most versatile and most implemented. The attributes that make these components preferable for many applications can be seen by looking at the 2N7000 vs. BS170 N-channel MOSFETs.
MOSFET Transistor Applications and Types
Transistors, including MOSFETs, are often used for signal amplification and essential switching operations. Applications where MOSFETs are regularly used include the following.
Typical MOSFET Transistor Applications:
- ☐ High-frequency circuit amplifiers
- ☐ In inverter circuits
- ☐ Voltage regulation
- ☐ Switch mode power supplies (SMPS)
- ☐ Chopper circuits
- ☐ Brushless DC (BLDC) motor drives
- ☐ In DC relay circuits
- ☐ Passive electronic component alternative
The list above is not exhaustive, but representative of the wide range of applications for MOSFETs. To fulfill these applications, there are various types of MOSFET utilization. Some of these are listed below.
MOSFET Technologies:
- Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)
CMOS technology is the basis for IC manufacturing of microprocessors (MPUs), microcontrollers (MCUs), DDR, and other memory chips, etc.
- Metal insulator semiconductor field effect transistors (MISFETs)
All MOSFETs are MISFETs, as silicon dioxide is used as the gate insulator material; however, other MISFETs may use a different dielectric.
- Double-diffused metal oxide semiconductors (DMOS)
DMOS devices utilize two different dopants that control the channel’s lateral rate of diffusion. Power MOSFETs are primarily constructed for this type of operation.
- Thin-film transistor (TFT)
TFTs are commonly used to manufacture video display screens.
- Floating-gate MOSFET (FGMOS)
FGMOSs consist of an isolated, floating gate. These components are used in memory cells.
In addition to the above, MOSFETs exhibit different performance characteristics dependent upon the class of operation.
MOSFET Classes and Operation
There are four classes of operation for MOSFETs, as shown in the figure below.
MOSFET N and P channel class symbols
As shown above, MOSFETs operate in either enhancement mode, where the channel is dynamically created during operation, or depletion mode, where the channel is preconstructed, devices. Both modes may be constructed using positively (P channel) or negatively charged (N channel) material.
Comparing the 2N7000 vs. BS170 N-Channel MOSFETs
Both the 2N7000 and BS170 are N-channel enhancement MOSFETs and have the following major features:
Features of the 2N7000:
Features of the BS170:
|
In addition to having similar features, these semiconductor components DMOS manufactured and are best suited for small current, lower power applications; such as servo control and switching. These devices can be compared based on their electrical and thermal characteristics, as listed below.
|
2N7000 vs BS170 Specifications Comparison |
||
|
Maximum Ratings |
2N7000 |
BS170 |
|
VDSS |
60V |
60V |
|
VDGR |
60V |
60V |
|
VGSS |
±20V |
±20V |
|
ID (continuous) |
200mA |
500mA |
|
PD |
400mW |
830mW |
|
Thermal Characteristics |
2N7000 |
BS170 |
|
Operating Range |
-55°C to 150°C |
-55°C to 150°C |
|
Thermal Resistance |
312.5°C/W |
150°C/W |
As indicated in the table, the BS170 has much better resistance to temperature changes and can carry a higher constant current. However, the 2N7000 uses less power. Additional specifications can be found in the 2N7000 and BS170 datasheets.
Creating the Best MOSFET PCBA Design
For the 2N7000 and BS170 MOSFETs, good design practices include following your PCBA contract manufacturer’s (CM’s) DFM, DFA rules, and guidelines should be instituted. However, to ensure the manufacturability and efficiency of your PCBA development process, you must rely upon a trusted industry component library resource for accurate and manufacturer-verified component symbols, footprints, and 3D CAD models for your chosen package type.
Suppose you’re looking for CAD models for common components or part comparisons like 2N7000 vs. BS170 N-channel MOSFETs. In that case, Ultra Librarian helps by compiling all your sourcing and CAD information in one place.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.