
Imagine high speed data communication between two boards, A and B, through a cable. Each board has a comparator to send and receive signals without any distortion. Now also imagine the cable is near a power motor next to it.
It is possible that the noise may interfere with the signal and may affect the operation of the receiving board. Now, the designer has to consider many factors such as toggle frequency, input signal range, and adjustable hysteresis for the hassle-free operation of the comparators. It’s a common challenge for designers working on triggering or Time of Flight applications.
In this regard, understanding the key elements of a high speed comparator design can help you avoid many post-design challenges. But, before diving deeper, let’s have some basic knowledge supplements.
What is a High Speed Comparator?
Comparators with a fast response time and small propagation delay (<100ns) are considered high speed comparators. High speed comparators are predominantly used in applications requiring fast data conversion, such as oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, oscilloscope probes, wave generators, semiconductor testers, etc.
Achieving a high speed comparator design is full of challenges. You can design comparator for two types of output:
- Open-collector output
- Push-pull output
High speed comparators are designed using push-pull output as open drain outputs have asymmetrical rise/fall times. The fastest push-pull comparator available in the market (such as TLV3601) has a 2.5 ns propagation delay coupled with 500 Mbps data output.
For applications requiring even faster data comparison, an LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling) output can be beneficial. Such comparators enable rapid rise and fall times with a low differential voltage swing of just 350 millivolts. Moreover, the system can achieve a data throughput of up to 4 Gbps with a propagation delay of just 250 picoseconds.
High Speed Comparator Design Elements
-
Signal Conditioning
For designing specialized applications requiring signal recovery, transmission, and trigger functions, such as an oscilloscope or a semiconductor tester, the designer has to look forward to the following key elements.
-
Toggle Frequency
Applications operating at higher frequencies require comparators with high toggle functions to quickly compare data input with the reference value. Some common examples of such applications are oscilloscopes and logic analyzers.
What is a toggle frequency?
It is the rate at which the comparator can switch from output high to output low. Unless the comparator has the min required toggle frequency, it will not be able to detect the incoming signal properly or may produce a distorted signal. High speed comparators have propagation delays close to 300ns to produce reliable and consistent waveforms closer to the origination point.
-
Hysteresis
Hysteresis in comparators tune out random noise. It allows the system to send data to multiple boards at a high frequency.
Some comparators (e.g., TLV3601) have fixed hysteresis, whereas some comparators (e.g., TLV3603) have on-chip adjustable hysteresis techniques. You may contact your design engineer to help select a suitable model for your application.
-
ToF applications
While designing Time of Flight (ToF) applications, pulse width detection, and input overdrive dispersion are two major elements of a high speed comparator design.
ToF applications make use of light or sound to detect the position of an object from the transmission point. Light pulse is sent from an LED towards the object and is reflected back to the receiver on to a photoelectric diode. There, the presence of a photoemissive comparator converts that photoelectric current to a voltage and is sent down the line to other connected equipment through a high speed comparator.
In the process, the received analog signal is converted to digital bits by an ADC to measure the distance and the object’s color and material type. In this regard, the high speed comparator design must meet the following standards for reliable results.
-
Reliable Pulse Width Detection Capacity
The laser drive used for sending the light has a specific wattage not to harm the retina of a person coming in between the source and the object.
The diagram below shows two separate pulse widths of the same wattage. The left one is narrower as it has traveled a long distance to fetch the object compared to the right one.
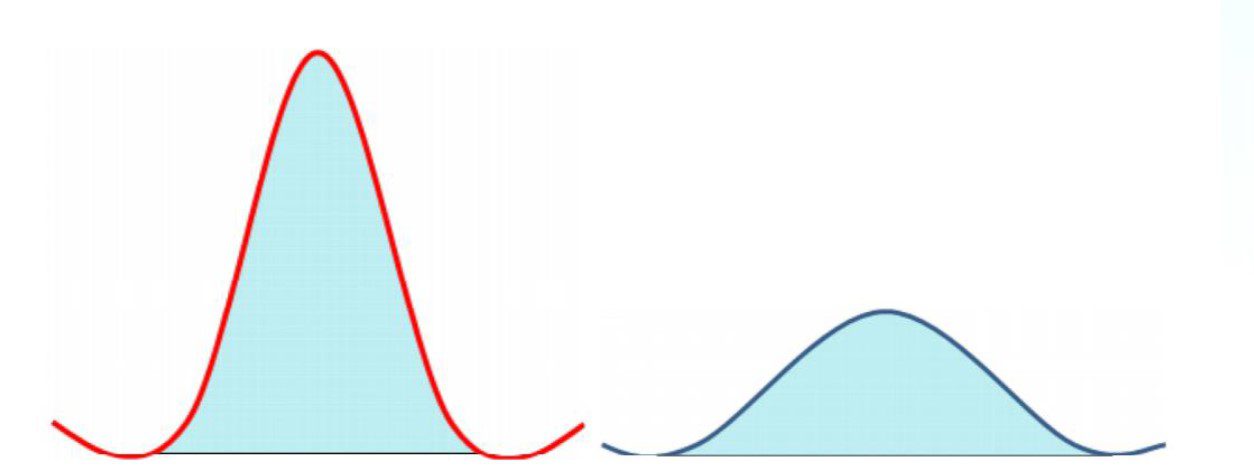
Unless the comparator at the receiving end has a wide pulse width detection capacity, it may not be able to acknowledge the signal at all. Again, this is directly related to toggle frequency of the comparator.
-
Input Overdrive Dispersion
Overdrive refers to the excess value of the input signal beyond the threshold limit of the comparator reference point. Dispersion is the propagation delay variance over a specific range of input overdrive.
Larger input overdrives result in faster response time. However, when the input overdrives go beyond 100 millivolts, the response time does not improve further – it tends to saturate.
In this regard, selecting a comparator with very low input overdrive dispersion ensures the correct measurement of object distance from the source irrespective of the amplitude of the reflected pulse.
Irrespective of the comparator you choose, understanding its datasheet, footprints, and 3D CAD models is imperative for a successful high speed comparator design. In this regard, the Ultra Librarian enables you to access all these pieces of information in one place.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.








