Gallium Nitride (GaN) semiconductor chip.
GaN technology is transforming how engineers design efficient and compact systems. It enables devices to operate at higher voltages and temperatures with improved thermal management, resulting in smaller and lighter power systems. These advantages align with the growing industry demands for performance, reliability, and sustainability across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and renewable energy. Compared to traditional silicon devices, GaN transistors deliver superior switching characteristics that enhance circuit performance. Faster transitions reduce heat buildup and enable higher operating frequencies, thereby reducing the size of passive components, such as capacitors. With continued advances in fabrication and wider commercial adoption, GaN is rapidly becoming the preferred material for next-generation power electronics.What is GaN technology and how it works
GaN technology is built on gallium nitride, a compound semiconductor with a wide bandgap of 3.4 eV, roughly three times greater than that of silicon. This wider bandgap gives GaN a much higher critical electric field, allowing devices to use thinner layers and shorter channels without electrical breakdown. In most power electronics, GaN is used to create enhancement-mode field-effect transistors (FETs). These are produced by growing a thin layer of gallium nitride on a silicon or silicon carbide substrate. At the junction between these materials, a two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) forms, providing a highly conductive channel where electrons move rapidly and with minimal scattering. This feature enables lower resistance, faster transitions, and reduced switching losses in comparison to silicon-based MOSFETs. Design engineers can choose between discrete GaN transistors and integrated power stages, depending on the system requirements. Discrete FETs are often used in high-voltage converters and inverters, while integrated devices combine drivers and protection circuits for simplified layouts and improved reliability.Benefits of GaN for Electronic Design
At the design level, gallium nitride technology enables the development of compact, efficient, and responsive power systems:- Power Density: By reducing switching and conduction losses, GaN devices achieve high power density while maintaining precise control over current flow. This lets engineers design converters and inverters that deliver more output power without increasing board area or thermal load.
- Size Reduction: Another major advantage of GaN technology is the ability to create smaller-sized components for high-frequency operations. GaN transistors switch rapidly, improving power conversion accuracy and reducing the size of passive components. The result is lighter, faster systems with improved transient response, an advantage in applications that demand consistent power quality.
- Reliability: GaN’s growing appeal in electronic design is in part due to its greater reliability. Its crystalline structure and wide bandgap allow stable electrical behavior even under high electric fields and extended temperature stress. This durability makes GaN suitable for long-lifespan systems in automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy applications where dependable operation is essential.
| Parameter | GaN (Gallium Nitride) | Silicon (Si) | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Design Impact |
| Bandgap Energy (eV) | 3.4 | 1.1 | 3.2 | A wider bandgap enables higher voltage operation and improved thermal stability. |
| Electron Mobility (cm²/V·s) | 2000 | 1500 | 900 | Faster switching speeds and higher efficiency in high-frequency circuits. |
| Breakdown Field (MV/cm) | 3.3 | 0.3 | 3.0 | Supports higher voltages and compact device geometries. |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 1.3–1.9 | 1.5 | 4.9 | SiC handles heat best, while GaN benefits from efficient thermal design. |
| Switching Frequency (kHz–MHz) | Up to several MHz | <100 kHz typical | 300–500 kHz | Enables smaller passive components and higher power density. |
| On-Resistance (mΩ·cm²) | Very low | Moderate | Low | Reduces conduction losses and increases efficiency. |
| Gate Charge (nC) | Low | High | Medium | Easier gate drive at high frequency, lowering driver losses. |

Gallium nitride powder and GaN power adapter.
Applications of GaN Technology
GaN technology is now established in both high-volume consumer products and specialized industrial systems. It plays an important role in how modern electronics manage, convert, and distribute power. Its expanding presence across multiple sectors reflects the industry’s shift toward advanced semiconductor materials that enable greater efficiency and sustainability.
Consumer and Portable Electronics
GaN has redefined what is possible in compact consumer devices and battery-powered systems. In fast chargers, adapters, and power supplies for laptops and smartphones, it enables high-efficiency power conversion at higher switching frequencies.
GaN-based USB-C chargers, for example, can deliver up to 100 W while remaining small enough to fit in a pocket. Beyond size reduction, these systems operate more efficiently, stay cooler, and offer longer component lifespans with improved user safety.
Data Centers and Industrial Power Systems
The growth of cloud computing and industrial automation has intensified the demand for power systems that deliver high output with minimal energy loss. GaN devices enable data center power supplies to reach exceptional efficiency, helping operators lower energy costs and reduce the thermal load on cooling systems.
This directly improves power usage effectiveness (PUE), a key performance metric for large-scale facilities. In industrial settings, GaN enhances motor drives, servo systems, and power converters by supporting faster control response and precise switching, resulting in compact, reliable, and responsive installations.
Automotive and Electric Mobility
In the automotive sector, GaN technology is accelerating the shift toward electric mobility by improving the efficiency of onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, and traction inverters. These systems regulate power flow between the battery and drivetrain, where even small efficiency gains can extend driving range and shorten charging times.
GaN’s fast-switching and compact structure allow for lighter modules with superior thermal management, supporting high power density without increasing cooling complexity. The technology also meets stringent automotive reliability standards such as AEC-Q101, ensuring stable performance in demanding environments.
Communications and RF Systems
Modern communication, telecom, and radar systems depend on high-frequency amplification to transmit and process large volumes of data. GaN transistors are widely used in 5G base stations, satellite transmitters, and radar arrays where high gain and power density are required. Their ability to operate efficiently at high frequencies supports faster data transmission and broader bandwidths, improving signal quality and system reliability in both terrestrial and aerospace networks.
Renewable Energy and Grid Applications
As renewable energy adoption grows, power conversion systems must deliver high efficiency and scalability. GaN devices meet these requirements in solar inverters, battery energy storage systems, and grid-tied converters by reducing conversion losses and improving transient response. These characteristics make GaN an ideal fit for distributed generation and smart grid systems that require precise power management, flexibility, and a reduced footprint.
While GaN technology continues to redefine what is achievable in power electronics, it still faces a few practical challenges. Manufacturing complexity, gate reliability, and heat dissipation at high power levels remain active areas of research and optimization. Ongoing advances in packaging methods and hybrid integration with silicon control circuits are steadily improving device reliability, cost-effectiveness, and scalability across applications.
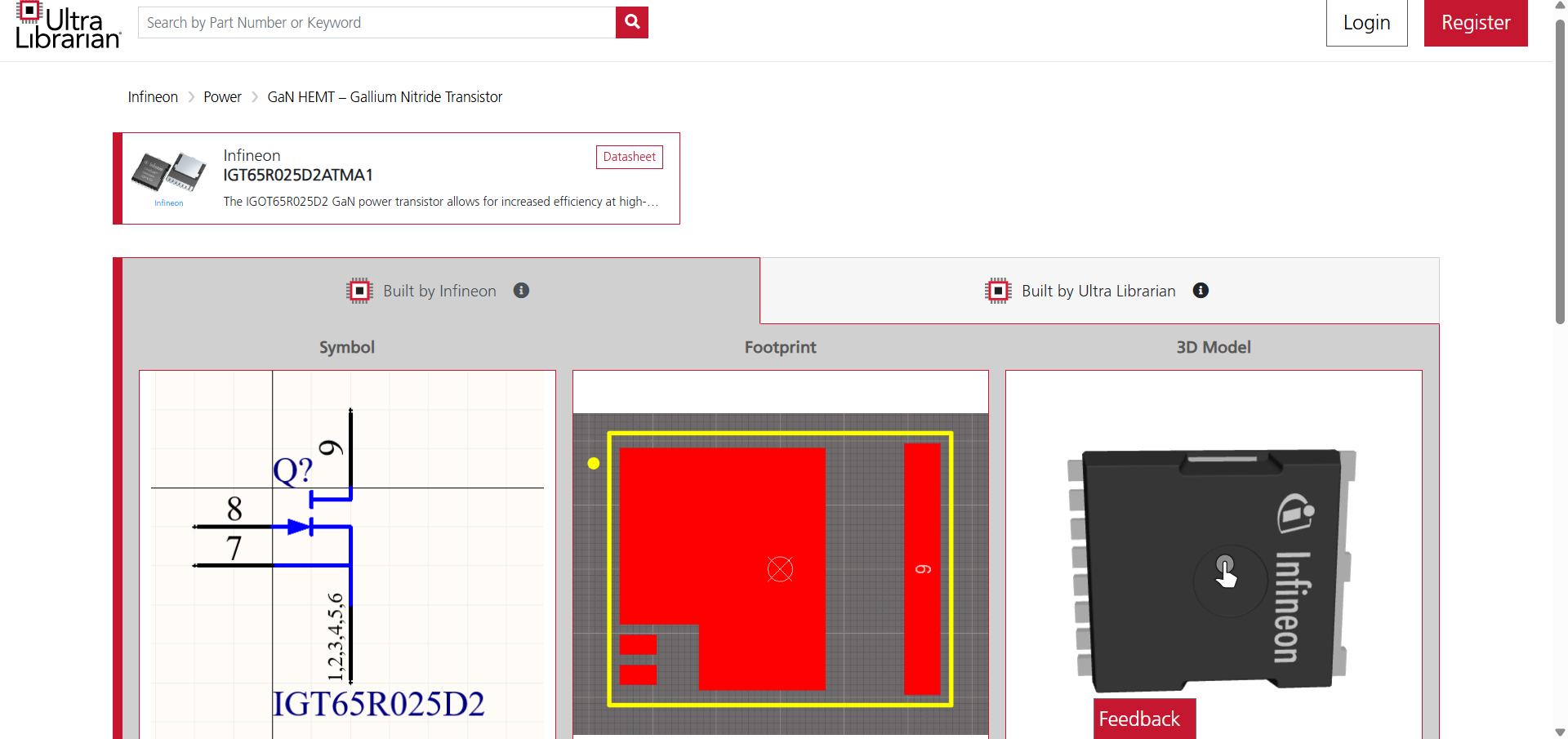
Infineon GaN transistor model, including symbol, footprint, and 3D view, in Ultra Librarian.
As GaN adoption accelerates, engineers need fast and reliable access to accurate component data to support design and sourcing decisions. If you’re looking for CAD models for GaN power transistors or other components used in power electronics, Ultra Librarian helps by compiling all your sourcing and CAD information in one place. You can also explore worldwide distributors directly through the platform.
Working with Ultra Librarian ensures that your team has the verified models needed for error-free design and production. Register today for free to explore verified CAD models and sourcing data for GaN power transistors and other advanced electronic components.