All circuit boards are built similarly, but there are many types of PCB material
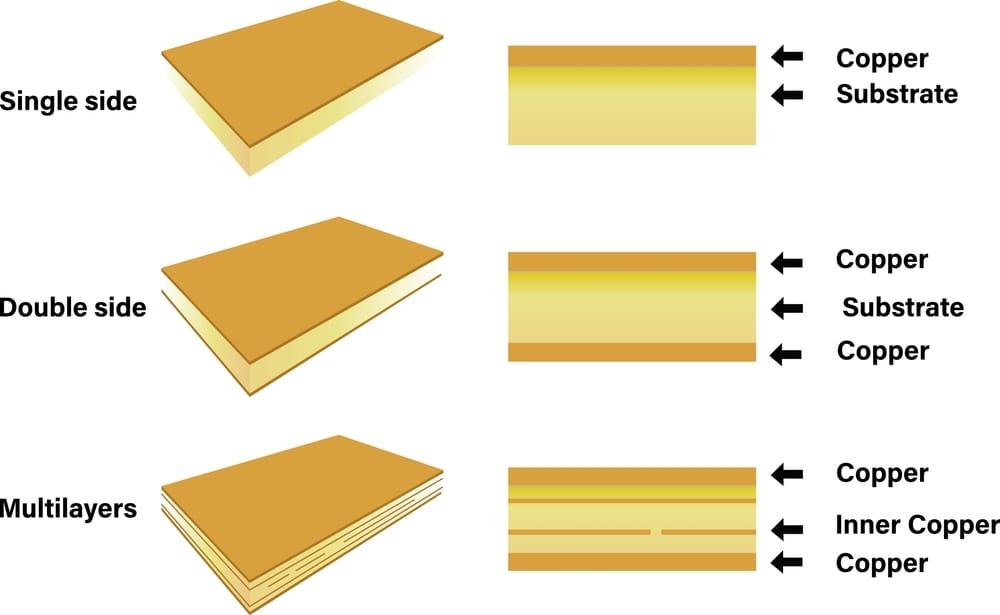
Circuit boards are often classified according to the number of layers in the PCB stackup. For example, single-sided, double-sided, or multilayer are common terms used to distinguish between different board design types. Rigid, flex, and rigid-flex are also familiar distinctions.
PCBs are also segmented in terms of application or usage; such as high-speed or automotive. Far less common, but probably more important, is to distinguish between circuit boards based on their electrical, thermal, mechanical, and/or chemical characteristics. Knowing the parameters that quantify these important characteristics is essential for selecting the board with the types of PCB material that is best for your design.
Different Types of PCB Material
Believe it or not, FR4 is not the only PCB material type available. This may not be obvious, as many PCBA design programs default to this popular board type. However, the explosion of circuit board utilization into smart products, IoT devices, industrial production facilities, space platforms, and other applications, are forcing engineers and PCB designers to investigate other types of PCB material, as listed below, in order to meet specific quality requirements.
|
TYPES OF PCB MATERIAL |
|
|
PCB Material Types |
Characteristics |
|
FR4 |
Most popular PCB material. Good general properties. |
|
FR5 |
High coefficient of temperature expansion (CTE). |
|
Polyimide |
Great flexibility and good tensile strength. |
|
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
Have consistent dielectric constant (Dk) and low dissipation factor (Df). |
|
Resin Coated Copper (RCC) |
Special material with uncured resin and copper foil used in high-density interconnect PCBs. |
|
Insulated Metal Substrate (IMS) |
Metal based PCB with excellent thermal dissipation. Good dielectric strength at high voltages. |
The list above is not exhaustive. However, the table clearly illustrates that PCB material properties can vary significantly. Your board’s operation, performance, durability, and reliability can be greatly impacted, if these attributes are not taken into account when selecting the type of PCB material for your design.
Choosing the Best Material for Your PCB
Knowing and understanding the parameters that specify PCB material properties is necessary to choose the best board material for your design, which is an important PCB layout best practice. This is done most effectively by grouping the parameters according to their area of impact. Below are the most important electrical, thermal, mechanical, and chemical parameters to know for the different types of PCB materials.
|
Important PCB Material Properties
|
If used effectively, the properties above can help you select the optimal type of PCB material to ensure your board not only achieves its functional and performance objectives, but also meets its quality requirements.
If you’re looking for CAD models for common components or important information about the best types of PCB material for your design, Ultra Librarian helps by compiling all your sourcing and CAD information in one place.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.